Poly Tuition
Ingel is the only tutor to teach university-level tuition and is here to help with polytechnic tuition, whether you are taking full-time or part-time diploma.
Read about Ingel’s credentials and his teaching style.
If you need some guidance in handling the tutorials, projects or assignments,
Call or WhatsApp Ingel at 96726733 now to avoid disappointment!

Hear From Our Student
One-to-one Classes Available
With students unable to adapt well to online classes, it is no surprise why more and more students are seeking tuition at diploma level.
Here are some common problems students are seeking help with:
- Programming – Python, R, Java, C++, Data Analytics
- Digital fundamentals – binary, JK flip-flops, asynchronous counters
- Financial accounting – future value of money, valuation, budgeting
- Operation management – utilization rate, inventory holding cost, supply-chain management, just-in-time
- Macroeconomics and microeconomics – fiscal policy, monetary policy, GDP, international trade, demand and supply, price elasticity
See testimonials from graduated poly students.
*Materials to be referenced from students’ notes.
**Topics will vary from one polytechnic to another.
The fees for Ingel’s polytechnic tuition range from 70 to 140 an hour.
Group Tuition Rates and Schedule

Poly Diploma
640/mth
2hr x 4 lessons
Sat 1.30pm – 3.30pm
Private Tuition Rates and Schedule

Poly Diploma
1120/mth
2hr x 4 lessons
Timing to be discussed
Assignment Help
Struggling with an assignment?
Ingel can help to provide guidance to resolve your frustrations.
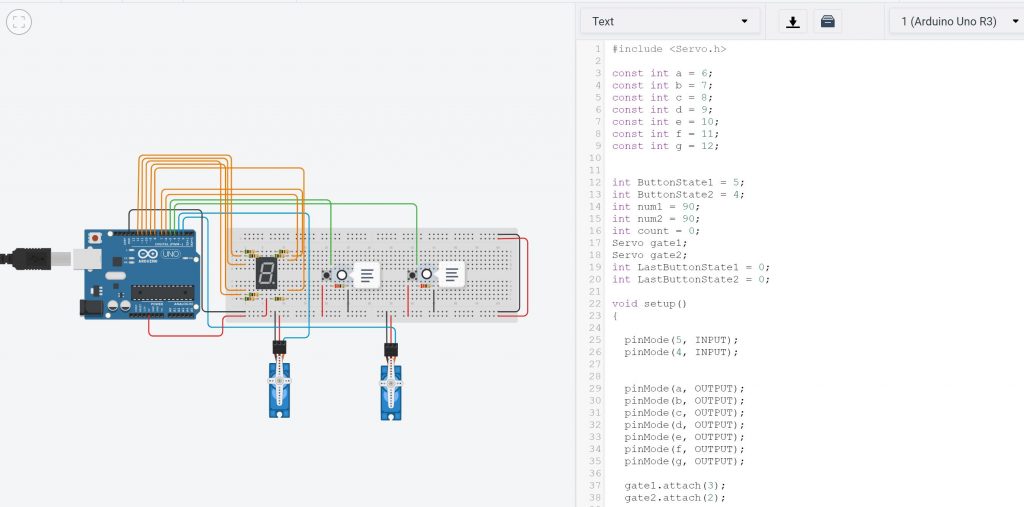
Example: Arduino Circuit
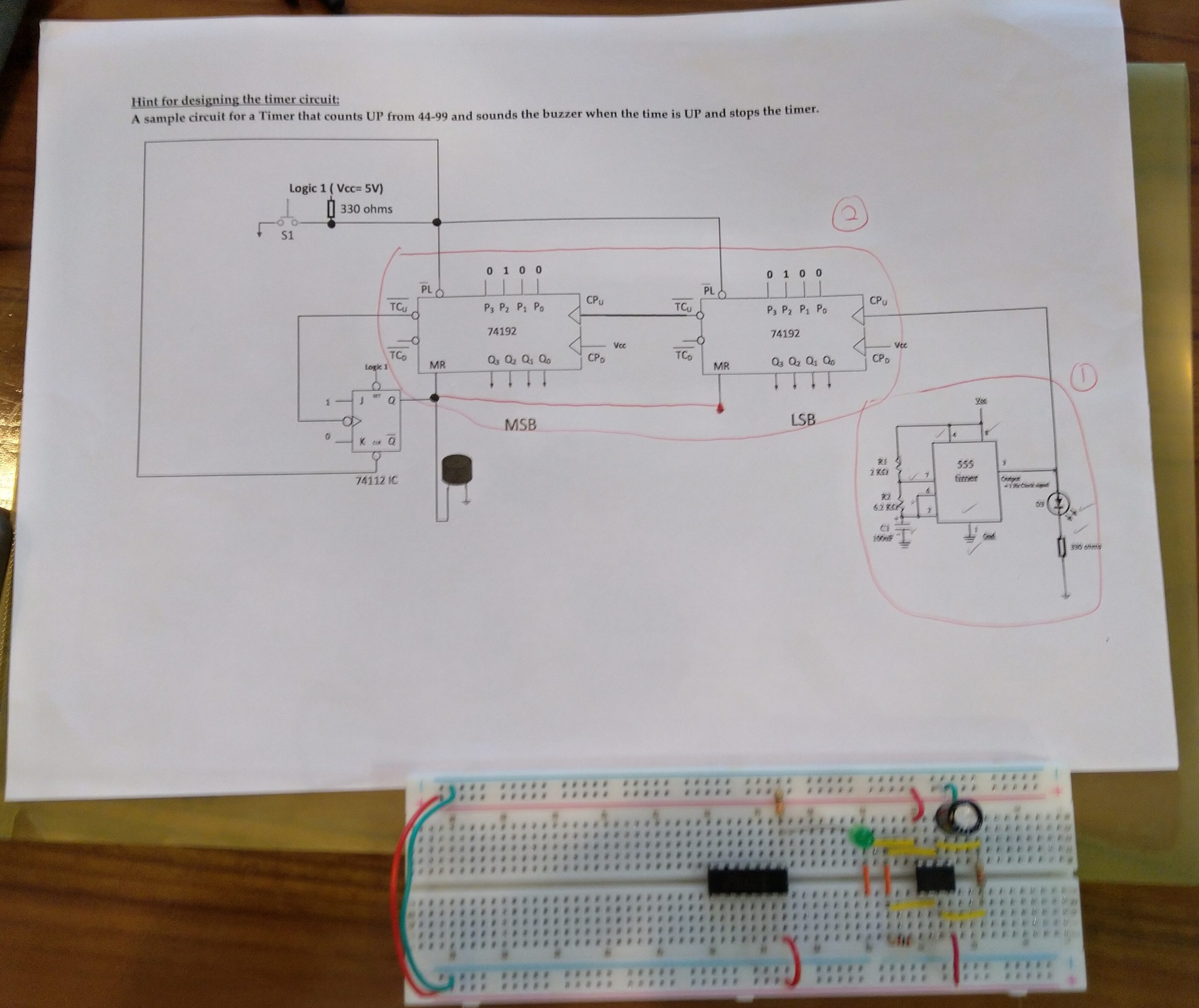
Example: Constructing a 555 Timer circuit
Poly Engineering Maths
- Algebra
- Calculus
- Differential Equations & Series
- Probability & Statistics
Accountancy & Finance
- Business Accounting
- Cost & Management Accounting 1
- Financial Accounting
- Principles of Management
- Business Technology & Analytics
- Business Economics
- Business Law
- Business Statistics
- Business Finance
- Cost & Management Accounting 2
- Fundamentals of Investment
- International Finance
- Company Accounting
- Fundamentals of Taxation
- Information Systems & Financial Analytics
- Corporate Reporting
- Financial Analysis
- Risk Management
- Auditing
- Practice of Taxation
- Advanced Accounting
- Financial Technology
- Personal Financial Planning
- Banking Products & Services
- Security Analysis & Portfolio Management
Aerospace Engineering
- Aircraft Electrical Fundamentals
- Aircraft Electronics & Digital Systems
- Engineering Drawing
- Circuit Analysis
- Electronic Devices & Circuits
- Digital Fundamentals
- Engineering Mathematics
- Statics & Strength of Materials
- Engineering Physics
- Computer Programming for Problem Solving
- Data Visualisation & Analytics
- Aviation Legislation & Human Factors
- Engineering Material
- Principles of Dynamics
- Thermodynamics
- Fluid Mechanics
- Gas Turbine Engine
- Basic Aerodynamics
- Aircraft Structures & Composites
- Aerospace Maintenance Practices
- Engine Maintenance & Workshop Practices
- Management and Organisation
- Professional and Technical Communication
- Introduction to Aviation
- Aviation Practice
- Quantitative Methods for Business
- Introduction to Aviation Management
- Introduction to Aviation Safety
Big Data and Analytics
- Logic & Mathematics
- Data Analytics
- Data Structures & Algorithms
- Computational Thinking
- User Experience & Interface Design
- Coding & Development Project
- Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence
- Data Science Essentials
- Quantitative Analysis
- Data Mining and Business Analytics
- Data Security & Governance
- Text & Social Media Analytics
- Applied Data Science in a Business Domain
- Web and Mobile Analytics
- Machine Learning for Developers
Business
- Business Accounting
- Principles of Management
- Organisational Behaviour
- Business Technology & Analytics
- Business Economics
- Economics in a Globalised World
- Business Law
- Business Statistics
- Marketing Fundamentals
- Business Finance
- Management Accounting
- Human Resource Management
- Managing Small & Medium Enterprises
- Enterprise Business Plan
- International Business
- International Finance
- Banking Products & Services*
- Fundamentals of Investment
- Personal Financial Planning
- Risk Management
- Security Analysis & Portfolio Management
- Enterprise Resource Management
- Customer and Social Media Analytics
- Business Systems & Innovation
- E-Commerce & Digital Marketing
- Business Development in IT
- Talent Acquisition & Management
- Total Rewards Management
- Learning & Talent Development
- Employment Laws
- Global Human Resource Management
- Human Resource Management in Practice
- Startup Launchpad
- Strategies in e-Business
- International Finance
- Business In Asia
- Product Development & Innovation
- Global Trade & Singapore Logistics
- Consumer Insights
Chemical Engineering
- Basic Microbiology
- Thermodynamics
- Mass and Energy Balance
- Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Principles of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry
- Engineering Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Environmental Technology
- Occupational Safety and Health
- Unit Operations
- Chemical Reaction Engineering
- Productivity Improvement
- Process Control and Instrumentation
- Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- Laboratory Analysis & Management
- Plant Safety and Loss Prevention
- Petrochemical Plant Processes
- GMP in Pharmaceuticals/ Biologics
- Biopharmaceutical Processing
Clean Energy
- Circuit Analysis
- Electronic Devices & Circuits
- Digital Fundamentals
- Electrical Services for Facilities
- Engineering Mathematics
- Engineering Physics
- Computer Programming for Problem Solving
- Data Visualisation & Analytics
- Fuel Cell & Energy Storage Systems
- Solar Cell & System
- Electrical Systems & Power Distribution
- Air Conditioning & Mechanical Ventilation
- Microcontroller Technology
- Energy Management & Audit
- Industrial Sustainability & Energy Efficiency
- Efficient Drive & Control Systems
- Electrical Diagnostics & System Integration
Financial Business Informatics
- Basic Business Finance
- IT Systems Security Essentials
- Database Application Development
- Logic & Mathematics
- Data Analytics
- Data Structures and Algorithms
- Computational Thinking
- User Experience & Interface Design
- Coding & Development Project
- Network Technology
- Banking Processes and Automation
- FinTech Innovations
- Open Banking App Development
- Mobile App Development
- Risk & Governance
- Wealth and Portfolio Management
- Digital Payment and Lending
- Distributed Ledgers and Blockchain
- Data Mining and Business Analytics
- Data Visualisation
- Database Application Development
Mechanical Engineering
- Computer-Aided Drafting
- Computer-Aided Drafting & Design
- Machine Elements & Mechanisms Design
- Statics & Dynamics
- Mechanics of Materials & Machines
- Engineering Materials
- CNC Turning Technology
- CNC Milling Technology
- Advanced Machining Processes
- Engine Technology
- Hydraulic System
- Electrical & Control System
- Thermofluid Systems
- Thermofluid Power
- Engineering Thermodynamics
- Industrial Automation
- Mechanical Assembly Process
- Mechanics of Machine Elements
Nanotechnology & Materials Science
- Electrical Principles & Circuits
- Mechanics – Statics
- Computer Programming
- Introduction to Engineering
- Communication Skills
- 3D Modelling
- Good Laboratory Practices
- Inorganic & Physical Chemistry
- Physics
- Materials Science
- General Studies
- Differential Equations & Series
- Probability & Statistics
- Thermodynamics
- Materials Analysis & Nanocharacterisation
- Organic Chemistry
- Polymers & Composites
- Metrology & Quality Control
- Advanced Materials Science
- Mechanics of Materials
- Micro & Nanotechnology
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship
- Materials & Nanotechnology Projects
- Nanomaterials Science
- Semiconductor Technology
- Nanomaterials & Commerce
- Electronic Materials
- Energy Harvesting & Storage
- Nanomaterials Science
- Advanced Crystalline Solids
- Nanomaterials & Commerce
- Smart Materials
- Electronic Materials
- Nanomaterials & Safety
- Energy Harvesting & Storage
- Sustainable Materials & Technology
- Nanomaterials & Commerce
- Semiconductor Technology
- Electronic Materials
- Nanomaterials & Safety
- Wafer Fabrication Processes
Systems Engineering
- Business Fundamentals
- Circuit Analysis
- Digital Fundamentals
- Engineering Mathematics
- Introduction to Processes & Systems
- Computer Programming for Problem Solving
- Data Visualisation & Analytics
- Systems Concepts & Tools
- Quantitative Methods
- Engineering Economy
- Service Quality & Management
- Process Management & Innovation
- Decision Analysis
- Process Optimisation & Improvement
- Manufacturing Logistics & Simulation
- Customer Relationship Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Systems Modelling & Simulation
Common Poly Engineering Terms
- Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity over time, typically measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
- Amplitude: The maximum value or magnitude of a waveform or oscillation, typically measured in volts (V).
- Circuit: A closed path through which an electric current flows, typically consisting of various components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
- Convection: The transfer of heat through a fluid (such as air or water) due to the movement of the fluid itself.
- Current: The flow of electric charge through a conductor, typically measured in amperes (A).
- Damping: The reduction of oscillation or vibration over time, typically caused by friction or other forms of resistance.
- Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance, typically measured in kilograms per meter cubed (kg/m^3).
- Elasticity: The ability of a material to return to its original shape after being subjected to stress or strain.
- Force: A measure of the interaction between two objects, typically measured in newtons (N).
- Frequency: The number of cycles per second of a periodic waveform or signal, typically measured in hertz (Hz).
- Impedance: The opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit, typically measured in ohms (Ω).
- Mass: The measure of the amount of matter in an object, typically measured in kilograms (kg).
- Power: The rate at which energy is transferred or consumed, typically measured in watts (W).
- Pressure: The force per unit area applied to an object, typically measured in pascals (Pa).
- Resistance: The opposition to the flow of electric current in a conductor, typically measured in ohms (Ω).
- Stress: The internal force per unit area within a material subjected to external forces, typically measured in pascals (Pa).
- Velocity: The rate of change of position over time, typically measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Voltage: The electric potential difference between two points, typically measured in volts (V).
- Volume: The amount of space occupied by an object, typically measured in meters cubed (m^3).
- Work: The transfer of energy through the application of force over a distance, typically measured in joules (J).
Common Poly Finance Terms
- Asset: A resource owned by an individual or organization that has monetary value, such as cash, stocks, or real estate.
- Balance sheet: A financial statement that reflects a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Capital: The financial resources or funds available for investment, typically including cash, securities, and other assets.
- Capital expenditure: An expenditure that is expected to generate benefits over a period of years, such as purchasing new equipment or property.
- Cash flow: The net amount of cash and cash-equivalents being transferred into and out of a business, typically including operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Debt: An obligation to pay a sum of money to another party at a later date, typically in the form of a loan or bond.
- Equity: The residual ownership interest in a company’s assets after all debts have been paid, typically representing the ownership stake of shareholders.
- Inflation: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling.
- Interest: The cost of borrowing money, typically expressed as a percentage of the principal amount borrowed.
- Investment: The allocation of money or capital to an asset or business with the expectation of generating income or capital appreciation.
- Liability: A legal obligation to pay a sum of money to another party at a later date, typically including debts and other financial obligations.
- Liquidity: The ability of an asset or security to be quickly bought or sold in the market without affecting the asset’s price.
- Margin: The amount by which an investor’s assets exceed the liabilities or debts, typically expressed as a percentage.
- Profit: The excess of revenue over expenses, typically representing the net income of a business.
- Rate of return: The percentage gain or loss on an investment over a specific period of time.
- Revenue: The total amount of income generated by a business from its sales or services, typically before expenses are deducted.
- Risk: The possibility of incurring losses or not achieving desired results, typically associated with investments or business ventures.
- Stock: A type of security that represents ownership in a company, typically entitling the holder to a share of the company’s profits and voting rights.
- Yield: The return on an investment, typically expressed as a percentage of the investment’s cost or market value.
Common Poly Economics Terms
- Demand: The desire to purchase goods and services, typically coupled with the ability and willingness to pay for them.
- Elasticity: The degree to which the quantity demanded or supplied of a good or service changes in response to changes in price or other factors.
- Gross domestic product (GDP): The total market value of all goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time, typically used as a measure of economic growth or size.
- Inflation: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling.
- Market: A system or network through which goods and services are exchanged, typically involving buyers, sellers, and prices.
- Opportunity cost: The next best alternative that must be given up as the result of a decision or action, typically expressed in terms of the cost of the alternative foregone.
- Price: The amount of money or other consideration asked in exchange for a good or service.
- Producer surplus: The difference between the price a producer receives for a good or service and the cost of producing it.
- Scarcity: The condition of not having enough resources to meet the demand for them, requiring individuals and societies to make choices about how to allocate them.
- Supply: The amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price.
- Utility: The satisfaction or pleasure received from consuming a good or service, typically used to measure the usefulness or value of an item to an individual.
- Value: The worth or importance placed on a good or service by an individual or society, typically expressed in terms of price or utility.
- Welfare: The well-being or prosperity of a group or society, typically measured by indicators such as income, education, health, and happiness.
Common Poly Marketing Terms
- Advertising: The practice of promoting a product, service, or brand through various media, such as television, radio, print, or online advertising.
- Branding: The practice of creating and promoting a unique name, design, or image for a product, service, or company to differentiate it from its competitors.
- Consumer: An individual or household that purchases goods or services for personal or household use.
- Customer: An individual or organization that purchases goods or services from a business or seller.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): The practice of managing and optimizing interactions with current and potential customers, typically involving the use of technology and data analytics to understand customer behavior and preferences.
- Direct marketing: The practice of promoting products or services directly to consumers through channels such as email, text message, or direct mail, rather than through mass media.
- Marketing mix: The set of variables that a company can control in order to influence demand for its product or service, typically referred to as the “four Ps”: product, price, place, and promotion.
- Positioning: The process of designing a product or service’s marketing strategy to occupy a clear, unique, and desirable position relative to its competitors in the minds of target consumers.
- Product: A tangible or intangible good or service offered by a company to its customers or clients.
- Promotion: The various activities and efforts undertaken by a company to communicate the benefits and value of its product or service to its target market.
- Public relations (PR): The practice of managing the flow of information between an organization and its stakeholders, typically involving the use of media relations, events, and other communications strategies to enhance the reputation and image of the organization.
- Sales: The act of exchanging a product or service for money or other forms of compensation, typically involving the efforts of a salesperson or team.
- Segmentation: The process of dividing a market into smaller groups of consumers with similar needs or characteristics, typically used to tailor marketing efforts and better target specific groups of consumers.
- Target market: The specific group of consumers or businesses that a company aims to reach and sell its products or services to.
Common Poly Accounting Terms
- Asset: A resource owned by an individual or organization that has monetary value, such as cash, stocks, or real estate.
- Balance sheet: A financial statement that reflects a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Capital: The financial resources or funds available for investment, typically including cash, securities, and other assets.
- Debt: An obligation to pay a sum of money to another party at a later date, typically in the form of a loan or bond.
- Equity: The residual ownership interest in a company’s assets after all debts have been paid, typically representing the ownership stake of shareholders.
- Expense: A cost incurred in the process of generating revenue, such as wages, rent, or supplies.
- Income statement: A financial statement that reflects a company’s revenues, expenses, and net income over a specific period of time.
- Liability: A legal obligation to pay a sum of money to another party at a later date, typically including debts and other financial obligations.
- Profit: The excess of revenue over expenses, typically representing the net income of a business.
- Revenue: The total amount of income generated by a business from its sales or services, typically before expenses are deducted.
- Accounting equation: The equation representing the relationship between a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, typically stated as “assets = liabilities + equity.”
- Accounts payable: The amount of money a company owes to its creditors or suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit.
- Accounts receivable: The amount of money a company is owed by its customers for goods or services provided on credit.
- Accrual: The recognition of revenues or expenses that have been earned or incurred, but have not yet been received or paid.
- Depreciation: The allocation of the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life, typically through periodic charges to expense.
- Double-entry accounting: An accounting system in which every transaction is recorded in at least two accounts, with the total debits equal to the total credits.
- Journal: A chronological record of a company’s financial transactions, typically used to record the initial entry of each transaction.
- Ledger: A record of a company’s financial accounts, typically consisting of a set of accounts for each type of asset, liability, equity, revenue, and expense.
- Trial balance: A report that lists the balances of all a company’s accounts as of a specific date, typically used to ensure that the total debits equal the total credits.
Common Poly Statistics Terms
- Average: A measure of central tendency that represents the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values, typically represented by the symbol “x̄”.
- Correlation: A statistical measure of the degree to which two variables are related, typically expressed as a correlation coefficient between -1 and 1.
- Distribution: The pattern or shape of a set of data, typically described by measures such as the mean, median, and standard deviation.
- Hypothesis testing: The process of using statistical methods to test a prediction or claim about a population, typically involving the construction of a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
- Mean: A measure of central tendency that represents the average of a set of values, typically calculated by summing the values and dividing by the number of values.
- Median: A measure of central tendency that represents the middle value of a set of values when the values are arranged in numerical order.
- Mode: A measure of central tendency that represents the most frequently occurring value in a set of values.
- Outlier: A data point that is significantly different from the rest of the data, typically identified as being more than a certain number of standard deviations from the mean.
- Population: The complete set of objects or individuals under study, typically represented by the symbol “N”.
- Probability: The likelihood of an event occurring, typically expressed as a decimal or fraction between 0 and 1
- Sample: A subset of the population, typically used to infer characteristics about the population based on statistical analysis of the sample.
- Standard deviation: A measure of dispersion or variability in a set of data, representing the average distance of the values from the mean.
- Statistic: A measure calculated from a sample, typically used to estimate a population parameter.
- Statistical inference: The process of making predictions or decisions about a population based on statistical analysis of a sample.
- Statistical significance: The probability that a statistical result is not due to chance, typically determined using a predetermined level of significance, such as alpha (α) = 0.05.
- Variable: A characteristic or attribute that can take on different values, typically divided into categorical and numerical variables.
Common Poly Chemistry Terms
- Acid: A substance that donates protons (H+) to a solution, typically having a sour taste and reacting with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
- Base: A substance that accepts protons (H+) from a solution, typically having a bitter taste and feeling slippery to the touch.
- Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
- Chemical reaction: A process that results in the transformation of one set of chemical substances into another.
- Compound: A substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio.
- Dilution: The process of reducing the concentration of a solution by adding solvent.
- Element: A pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, typically consisting of a single type of atom.
- Ion: An atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a positive or negative charge.
- Isotope: A variant of an element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in its nucleus, resulting in a different atomic mass.
- Molecule: A group of atoms bonded together, typically representing the smallest unit of a compound that retains the chemical properties of the compound.
- Neutralization: The process of reacting an acid with a base to produce a salt and water, typically resulting in a neutral solution with a pH of 7.
- Oxidation: The process of losing electrons during a chemical reaction, typically resulting in an increase in oxidation state.
- PH: A measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, typically expressed on a scale of 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
- Reduction: The process of gaining electrons during a chemical reaction, typically resulting in a decrease in oxidation state.
- Salt: A compound formed by the reaction of an acid with a base
- Solvent: A substance that dissolves a solute to form a solution.
- Solute: A substance that is dissolved in a solvent to form a solution.
- Solution: A mixture of two or more substances in which the molecules of the solute are evenly distributed throughout the solvent.
- Sublimation: The process of a solid transitioning directly to a gas without passing through a liquid phase.
- Suspension: A mixture in which the particles of the solute are not evenly distributed throughout the solvent and tend to settle to the bottom.
- Volume: The amount of space occupied by a substance, typically measured in liters (L) or milliliters (mL).
- Weight: The measure of the force exerted on an object due to gravity, typically measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
Common Poly Biology Terms
- Adaptation: The process by which a species changes over time in response to its environment, allowing it to better survive and reproduce.
- Cell: The basic unit of life, typically consisting of a membrane-bound structure that contains DNA and other molecules required for life.
- Chromosome: A structure found in the nucleus of cells that contains DNA and proteins, and is involved in the transmission of genetic information during reproduction.
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): A molecule that stores genetic information and is passed from parent to offspring during reproduction.
- Evolution: The process by which species change over time through natural selection, resulting in the adaptation of organisms to their environment.
- Gene: A unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA, encoding a specific trait or function.
- Genome: The complete set of genetic information contained in an organism’s DNA, typically representing all the genes of an organism.
- Heredity: The transmission of genetic characteristics from parent to offspring through the genetic material (DNA).
- Metabolism: The chemical processes that occur within an organism to maintain life, typically involving the conversion of energy and matter.
- Mutation: A change in the DNA sequence of a gene or genome, typically resulting in a change in the trait or function encoded by the gene.
- Nucleotide: The basic unit of DNA and RNA, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- Organism: A living being, such as a plant, animal, or microbe, that is capable of reproducing, growing, and maintaining homeostasis.
- Phenotype: The physical and behavioral characteristics of an organism, typically resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
- RNA (ribonucleic acid): A molecule involved in the synthesis of proteins, consisting of a single strand of nucleotides that is complementary to a specific DNA sequence.
- Species: A group of organisms that are capable of interbreeding and producing viable offspring, typically representing a distinct evolutionary lineage.
- Trait: A characteristic or attribute of an organism, typically inherited through its genetic material (DNA).
- Variation: The differences that exist among individuals within a population, typically resulting from genetic and environmental factors.
Common Poly Physics Terms
- Acceleration: The rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time, typically measured in meters per second squared (m/s²).
- Atom: The basic unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons.
- Charge: A property of matter that determines the electrical behavior of an object, typically measured in coulombs (C).
- Conservation of energy: The principle that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant, regardless of the changes that occur within the system.
- Electric field: The region around a charged object in which another charged object experiences a force, typically represented by lines of force.
- Electric potential: The potential energy per unit of charge associated with a charged object or a point in an electric field, typically measured in volts (V).
- Electricity: The flow of electric charge through a conductor, typically resulting in the transfer of energy.
- Energy: The capacity to do work or produce change, typically measured in joules (J).
- Force: A push or pull on an object, typically measured in newtons (N) and acting to change the motion of the object.
- Frequency: The number of times a periodic event occurs within a specific time interval, typically measured in hertz (Hz).
- Gravity: The force that attracts two objects with mass towards each other, typically proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Ion: An atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a positive or negative charge.
- Mass: The measure of the amount of matter in an object, typically measured in kilograms (kg).
- Matter: Anything that occupies space and has mass, consisting of atoms and their constituent particles.
- Momentum: The product of an object’s mass and velocity, typically representing the amount of motion possessed by the object.
- Nucleus: The central core of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons and surrounded by electrons.
- Particle: A fundamental unit of matter, such as an electron, proton, or neutron.
- Periodic motion: The repetitive back-and-forth or circular motion of an object, typically characterized by a period, frequency, and amplitude.
- Photon: A quantum of electromagnetic radiation, typically characterized by its frequency, wavelength, and energy.
- Power: The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred, typically measured in watts (W).
- Proton: A subatomic particle with a positive charge and a mass slightly less than that of a neutron, found in the nucleus of an atom.
- Radiation: The emission of energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic particles, typically resulting from the decay of radioactive materials or the acceleration of charged particles.
- Sound: A type of mechanical wave that travels through a medium, typically characterized by its frequency, wavelength, and amplitude and perceived as a sensation of hearing.
- Velocity: The rate of change of an object’s position with respect to time, typically measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Wave: A disturbance that travels through space and time, typically characterized by its frequency, wavelength, and velocity and described using mathematical equations.
- Work: The transfer of energy from one object to another or the transformation of energy from one form to another, typically measured in joules (J) and defined as the product of force and displacement.
Common Poly Math Terms
- Algebra: A branch of mathematics in which symbols and variables are used to represent quantities and express relationships, typically involving the manipulation of equations and inequalities.
- Angle: A figure formed by two rays or line segments that have a common endpoint, typically measured in degrees or radians.
- Arithmetic: The branch of mathematics that deals with the manipulation of numbers, typically involving operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Calculus: A branch of mathematics that deals with the study of rates of change and the summation of infinitely many small quantities, typically involving the concepts of derivatives and integrals.
- Coordinate: A set of numbers that represents the position of a point in space, typically used to specify the location of a point in a coordinate system.
- Coordinate system: A system for specifying the position of a point in space using a set of coordinates, typically represented by an origin, a set of axes, and a unit of measurement.
- Equation: A mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions, typically involving one or more variables and requiring the solution of the variables to determine the truth of the statement.
- Exponent: A number that indicates the number of times a quantity is multiplied by itself, typically represented by a superscript or raised to a power.
- Geometry: A branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids, typically involving the use of axioms and theorems to deduce new results.
- Inequality: A mathematical statement that asserts the relative magnitude of two expressions, typically involving one or more variables and represented by symbols such as “≤”, “≥”, “<“, or “>
- Integral: A mathematical operation that represents the summation of infinitely many infinitesimally small quantities, typically used to find the area under a curve or the volume of a solid.
- Limit: The value that a function approaches as the independent variable approaches a particular value, typically used to define the derivative of a function.
- Logarithm: The exponent to which a base must be raised to produce a given number, typically represented as the logarithm of the number to the base.
- Matrix: A rectangular array of numbers, typically used to represent linear transformations or systems of linear equations.
- Number: A symbol or set of symbols used to represent a quantity, typically involving the counting numbers, the zero, and the negative integers.
- Probability: The likelihood of an event occurring, typically expressed as a decimal or fraction between 0 and 1.
- Radian: A unit of angular measure equal to the angle subtended by an arc of a circle whose length is equal to the radius, typically used in calculus and physics.
- Set: A collection of objects or elements, typically represented by listing the elements within curly braces or using set notation.
- Trigonometry: A branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles, typically involving the use of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
Locations
Tampines

*Pets (Kobe and Truffles) can be requested to be caged or free-roamed
Block 432 Tampines Street 41, Singapore 520432
Nearest MRT: Tampines East Station (Downtown Line)
Contact
WhatsApp/Telegram: +65 96726733